Last Updated on January 23, 2025 by Arif Chowdhury
Cholesterol. It’s something that everyone hears about at one point or another, especially as we age or when we have regular check-ups. But what does it really mean for your health?
The answer isn’t always black and white. While cholesterol is essential for various body functions, having too much of the wrong kind can raise your risk of heart disease and stroke.
Thankfully, you don’t need to resort to medication right away to manage your cholesterol levels. The Mediterranean diet, celebrated for its rich flavors and health benefits, offers a natural and effective way to lower cholesterol and improve heart health.
In this article, we’ll explore how the Mediterranean diet works, how it can help lower your cholesterol, and why it might just be the lifestyle change you’ve been looking for.
What Is Cholesterol, and Why Does It Matter?
Before diving into the Mediterranean diet, let’s quickly touch on cholesterol itself. Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in your blood, and it’s produced by your liver.
It plays an essential role in building healthy cells, but too much of it—especially the wrong type—can be harmful. There are two main types of cholesterol:
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein): Often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, high levels of LDL can lead to plaque buildup in your arteries, which increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein): Known as “good” cholesterol, HDL helps remove LDL from your bloodstream, reducing the risk of heart problems.
According to the American Heart Association, nearly 95 million American adults have total cholesterol levels higher than recommended, which can contribute to serious heart conditions.
The Mediterranean Diet: A Natural Solution
The Mediterranean diet is based on the traditional eating habits of people living in countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, such as Greece, Italy, and Spain.
It’s not just a diet but a lifestyle that emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, healthy fats, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. So, how exactly can it help with lowering cholesterol?
1. Emphasis on Healthy Fats
One of the Mediterranean diet’s key features is its focus on healthy fats, particularly monounsaturated fats and omega-3 fatty acids. These fats are known to reduce LDL cholesterol and boost HDL levels. Here’s a breakdown:
- Olive oil: The cornerstone of Mediterranean cooking, olive oil is a rich source of monounsaturated fats. It has been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol levels and lower the risk of heart disease.
- Nuts and seeds: Walnuts, almonds, and flaxseeds are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which help increase HDL cholesterol while reducing LDL levels.
- Fatty fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3s, which can lower triglycerides and inflammation in the body, further contributing to healthy cholesterol levels.
In fact, a study from the New England Journal of Medicine found that individuals on a Mediterranean diet supplemented with extra virgin olive oil saw a 30% reduction in heart disease risk compared to those on a low-fat diet.
2. A Rich Array of Plant-Based Foods
A Mediterranean diet is loaded with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts. These plant-based foods are naturally high in fiber, antioxidants, and other nutrients that support heart health.

- Fiber: Found in foods like beans, lentils, and whole grains, fiber helps lower cholesterol by binding to bile acids and removing them from the body. This process forces the liver to use up cholesterol to make more bile, thereby lowering overall cholesterol levels.
- Antioxidants: Fruits and vegetables like berries, tomatoes, and leafy greens are packed with antioxidants that protect the blood vessels from oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which can contribute to heart disease.
- Whole grains: Switching from refined grains to whole grains (like quinoa, brown rice, and barley) has been shown to lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health.
Research suggests that people who follow plant-heavy diets, like the Mediterranean diet, have lower levels of total cholesterol and are less likely to develop heart disease.
3. Reduced Consumption of Processed Foods and Red Meat
The Mediterranean diet encourages cutting down on processed foods, refined sugars, and red meats, which are high in unhealthy fats and salt. Instead, the focus is on consuming lean proteins, such as chicken and fish, and plant-based sources of protein like beans and legumes.
- Less processed meat: Studies show that reducing the intake of processed meats (like sausages and bacon) lowers LDL cholesterol and reduces the risk of heart disease.
- Lower sodium: Cutting back on salt helps control blood pressure, a significant risk factor for heart disease.
By focusing on whole, natural foods, the Mediterranean diet helps balance cholesterol levels and lowers the risk of heart-related complications.
How the Mediterranean Diet Impacts Cholesterol Levels
Now, let’s look at how these dietary changes translate into real-world benefits for cholesterol:
- Increased HDL: The healthy fats in olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish are all linked to higher levels of HDL cholesterol, the “good” cholesterol that helps clear excess LDL from your bloodstream.
- Decreased LDL: The high fiber content from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains helps lower LDL cholesterol, especially when combined with the healthy fats in the diet.
- Lower triglycerides: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish and certain nuts, are known to reduce triglyceride levels, which are another risk factor for heart disease.
According to a study published in The Lancet, people who followed the Mediterranean diet for three years experienced a reduction in LDL cholesterol levels by up to 8%. This is a significant drop that can have long-term health benefits.
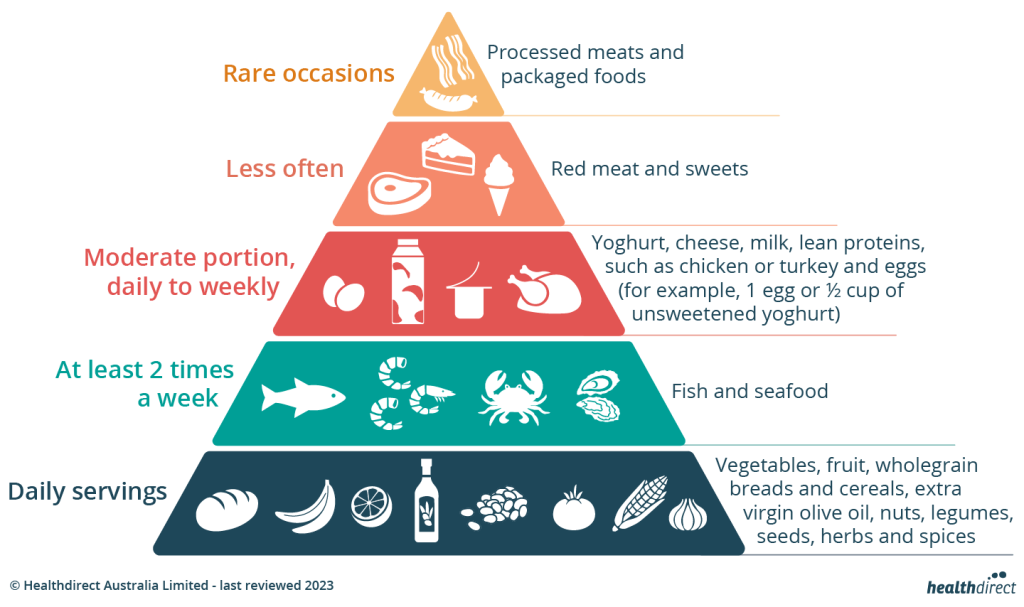
A Mediterranean Diet Plan to Lower Cholesterol Naturally
If you’re looking to adopt the Mediterranean diet to lower cholesterol, here’s a simple guide to get started:
Breakfast
- Whole grain toast with avocado and a drizzle of olive oil.
- Greek yogurt topped with fresh berries and walnuts.
- Oatmeal with chia seeds and sliced almonds.
Lunch
- A Mediterranean salad with mixed greens, tomatoes, cucumbers, olives, feta cheese, and a generous pour of olive oil.
- Whole grain wrap with hummus, roasted vegetables, and a sprinkle of sunflower seeds.
Dinner
- Grilled salmon with quinoa and steamed broccoli.
- Stir-fried vegetables with chickpeas and a side of brown rice.
- Baked chicken with roasted sweet potatoes and sautéed spinach.
Snacks
- A handful of almonds or walnuts.
- Fresh fruit, such as an apple or orange.
- Carrot sticks with hummus.
Scientific Backing: Why It Works
The Mediterranean diet isn’t just a trendy way of eating—it’s backed by science. Numerous studies have shown that following this eating pattern can help lower cholesterol and reduce heart disease risk. According to the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, individuals who follow a Mediterranean diet experience a 25% reduction in the risk of cardiovascular events, including strokes and heart attacks.
Additionally, a study published in Circulation found that those who adhered to the Mediterranean diet had significantly lower levels of total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol over time.
A Heart-Healthy Change Worth Making
Incorporating the Mediterranean diet into your lifestyle is a powerful way to lower your cholesterol naturally. By focusing on whole foods, healthy fats, and a plant-based approach, you can improve your heart health and feel your best.
And the best part? It’s not just good for your cholesterol—it’s an enjoyable, sustainable way of eating that promotes overall well-being.
If you’re looking for a heart-healthy change that’s easy to follow and backed by research, the Mediterranean diet might be the perfect solution. With its emphasis on fresh, delicious, and nutrient-rich foods, it’s a diet you can stick with for the long haul.
