Last Updated on January 23, 2025 by Arif Chowdhury
The ketogenic (keto) diet has become a popular trend in the world of health and fitness over the past few years. It’s a low-carb, high-fat diet designed to push the body into a state called ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates.
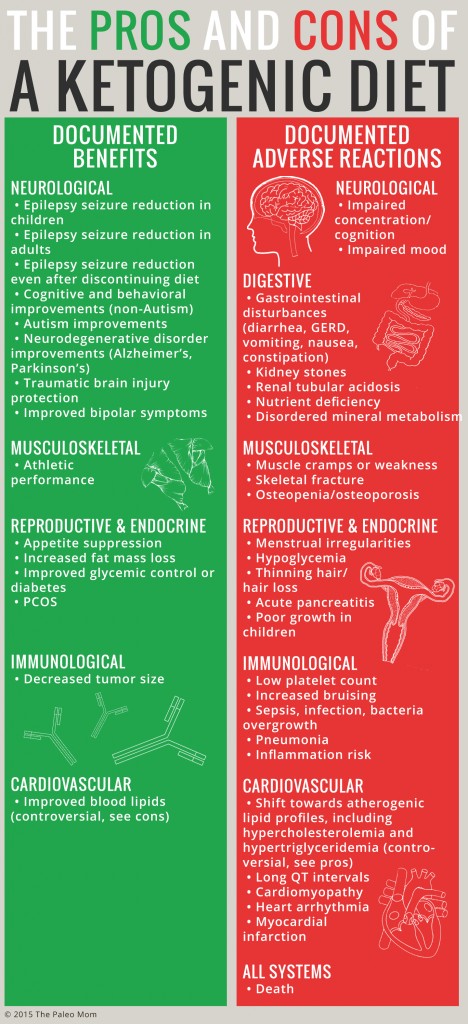
Many people have seen impressive results from following this diet, including weight loss and improved energy levels. However, like any dietary change, the keto diet comes with its own set of side effects that are worth considering before jumping in.
In this article, we’ll explore some of the potential side effects of the keto diet, backed by research and statistics.
Whether you’re considering starting the diet or are already following it, understanding both the benefits and challenges is essential to making an informed decision.
What is the Keto Diet?
Before diving into the side effects, let’s quickly review what the keto diet is all about. The keto diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and very low-carbohydrate eating plan. The typical macronutrient breakdown looks something like this:
- 70–80% of calories from fat
- 20–25% of calories from protein
- 5–10% of calories from carbohydrates
This extreme reduction in carbs forces the body to enter ketosis, a metabolic state where the liver produces ketones to be used as an alternative energy source.
In ketosis, fat is burned more efficiently than carbs, which is why the keto diet is often linked to weight loss and improved fat metabolism.
However, this dramatic shift in metabolism can also lead to some temporary or even long-term side effects that you should be aware of.
The “Keto Flu” – A Common Side Effect
When transitioning to the keto diet, many people experience what’s commonly known as the “keto flu.” This set of symptoms occurs as your body adapts to burning fat for fuel instead of carbs. It usually happens within the first few days of starting the diet and can last anywhere from a few days to a week.
Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Nausea
- Dizziness
- Brain fog
Approximately 25% of people on the keto diet report experiencing the keto flu to some extent. While these symptoms can be uncomfortable, they typically go away after the first week as your body adapts to ketosis.
Staying hydrated and replenishing electrolytes (like sodium, potassium, and magnesium) can help reduce the severity of the keto flu.
Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalance
The keto diet has a natural diuretic effect on the body, meaning it causes you to urinate more frequently.
As you reduce your carb intake, your body holds onto less water and releases it more quickly. This can lead to dehydration, which in turn may cause symptoms like headaches, muscle cramps, and fatigue.
In addition to dehydration, the loss of water also leads to a loss of essential electrolytes. Sodium, potassium, and magnesium are important for maintaining muscle function, hydration, and nerve function.
Without these electrolytes, you may experience symptoms like muscle cramps or irregular heart rhythms.
Studies show that about 63% of keto dieters report an electrolyte imbalance in the first few weeks.
To prevent dehydration and electrolyte deficiency, it’s recommended to drink plenty of water and consume foods rich in these minerals, such as avocados, leafy greens, nuts, and seeds. You can also consider electrolyte supplements if necessary.
Constipation – A Possible Keto Side Effect
Another side effect that many people face while on the keto diet is constipation. Since the keto diet is so low in fiber (due to the restriction of carbs), your digestive system may struggle with regular bowel movements. This can be uncomfortable and frustrating for many people.
According to a 2018 study published in The Journal of Clinical Medicine, about 40% of people on the keto diet experience constipation. The lack of fiber-rich foods like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables can make it difficult to maintain proper digestive health.
To combat this side effect, try increasing your fiber intake with keto-friendly high-fiber foods, such as chia seeds, flaxseeds, and low-carb vegetables like spinach, zucchini, and cauliflower. Drinking plenty of water can also help soften stool and improve bowel regularity.
Increased Cholesterol Levels
One of the most controversial aspects of the keto diet is its potential effect on cholesterol levels. Since the diet is high in fat, many people worry that it could raise their cholesterol, particularly their LDL (“bad”) cholesterol.
While research on this topic is still ongoing, some studies have found that the keto diet can lead to higher cholesterol levels, especially in the short term.
For example, a study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that the keto diet led to a significant increase in LDL cholesterol levels in some participants.
However, it’s worth noting that the keto diet can also increase HDL (“good”) cholesterol and lower triglycerides, both of which are beneficial for heart health.
The impact on cholesterol varies from person to person, and some people may experience an increase in LDL cholesterol while others do not. If you’re concerned about cholesterol, it’s a good idea to get regular blood tests to monitor your levels and discuss them with your healthcare provider.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Because the keto diet restricts certain food groups, there is a potential risk for nutrient deficiencies if it’s not carefully planned.
For example, since the diet limits fruits, starchy vegetables, and grains, it can be difficult to get enough of certain vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, potassium, and magnesium.
In fact, a study in The Journal of Nutrition found that 40% of individuals on the keto diet had insufficient levels of magnesium, which is essential for muscle function, energy production, and bone health.
Additionally, limiting dairy and leafy greens can reduce calcium and vitamin K intake, which are important for bone health.
To minimize the risk of nutrient deficiencies, it’s essential to eat a variety of nutrient-dense, low-carb foods. You might also consider taking supplements to ensure you’re getting all the essential vitamins and minerals your body needs.
Bad Breath – A Surprising Keto Side Effect
Bad breath, often referred to as “keto breath,” is a common side effect of the keto diet. This happens because, in ketosis, the body produces acetone, a type of ketone that is exhaled through the breath.
While it’s not harmful, it can lead to an unpleasant odor that some people find bothersome.
Approximately 20% of people on the keto diet report experiencing bad breath. Drinking plenty of water, chewing sugar-free gum, and practicing good oral hygiene can help alleviate the problem.
Some people also find that incorporating more minty herbs like parsley or basil into their meals can freshen their breath.
Is the Keto Diet Right for You?
The keto diet can be a powerful tool for weight loss and improving certain health markers, but it isn’t for everyone. It’s essential to weigh the potential benefits against the side effects and decide if it’s a good fit for your lifestyle and health goals.
Remember, everyone’s body responds differently to dietary changes. Some people thrive on keto and experience little to no side effects, while others may struggle with the adjustment.
It’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist before starting any new diet, especially one as restrictive as keto.
Understanding Keto’s Side Effects
The keto diet can offer incredible benefits, including weight loss, improved energy levels, and better blood sugar control.
However, it’s not without its side effects. From the keto flu to potential nutrient deficiencies, it’s important to understand what you might experience when starting the diet.
If you’re considering the keto diet, keep in mind that it’s essential to stay hydrated, replenish electrolytes, and make sure you’re eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods. With careful planning, you can minimize the negative side effects and get the most out of the keto lifestyle.
